If you’ve ever turned on the tap and had something that looked (and smelled) a bit off, you were likely experiencing water with Total Dissolved Solids (TDS). TDS is simply a measure of all the dissolved solids in water.
But what does that mean for your everyday life? And how do you calculate it? So let’s take a closer look.
What Is TDS in Water?
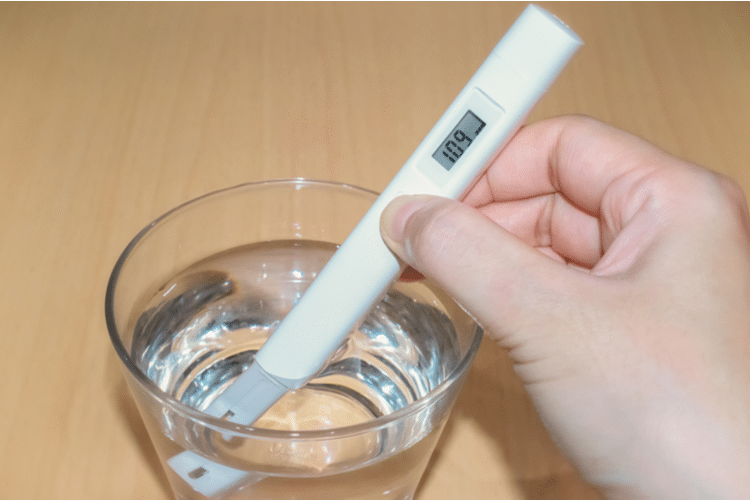
TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids. It measures the total amount of soluble minerals and salts in water. For example, if you have a water pitcher with one mg/L TDS, there is one mg/L of dissolved minerals in your water pitcher.
What’s important to know is that TDS isn’t just a measure of the total amount of dissolved solids in water. It also includes minerals, salts, and metals dissolved in the water.
So you can’t just get TDS by adding up all the different kinds of dissolved solids – you need to calculate it separately for each type!
How Does TDS Get in Water?
There are three main ways TDS can get into your water: from the water itself, from the air, and the ground. For example, some cities and towns treat their water with chemicals to kill bacteria and other harmful organisms.
These chemicals are called disinfectants. But these disinfectants can also end up getting into your water supply, especially if they’re leftover after the treatment process is done.
If you see a lot of white sediment or foam in your water pitcher, there’s chlorine or chloramine in your tap water. Chlorine makes tap water taste great (and smell great), but it can react with certain organic compounds to form substances like trihalomethanes (THMs).
These substances are not only unhealthy for you to drink, but they also have been linked to many serious health problems, including cancer and congenital disabilities.
List of Organic & Inorganic Total Dissolved Solids in Water
The following is a list of organic and inorganic total dissolved solids in water, organized by type.
Organic:
- Carbonates
- Bicarbonates
- Organic acids
- Amino acids
- Proteins
- Sugars
- Urea
Inorganic:
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chloride
- Sulfate
- Phosphate
- Carbon dioxide
While all water contains dissolved solids, the levels of these solids vary depending on the source. For example, groundwater typically has higher levels of dissolved minerals, while surface water from rivers and lakes tends to have lower levels.
Water that has been treated with a reverse osmosis system also typically has very low levels of dissolved solids.
Normal TDS of Drinking Water in PPM
The TDS values for different water sources vary depending on whether the water is naturally occurring or comes from a treatment facility. There are many ways to measure TDS, with the most common being by a titration method.
Titration is done by mixing known amounts of distilled water with a solution containing dissolved solids. The amount of solid that dissolves into the solution is then determined and compared to a standard reference table.
Aqueous solubility: carbon dioxide (CO), sulfate, chloride, potassium chloride, heavy metals, and radon can dissolve in water; they are present in small amounts that are usually not harmful to human health because they are rapidly removed from drinking water by filtration or activated carbon treatment.
These substances do not pose any threat to health because their concentration in drinking water is too low to cause any adverse health effects. In addition, some of these substances are naturally occurring and present in ground and surface water as a natural component of the water.
The EPA has set the highest contaminant levels for some contaminants in drinking water. The MCLs generally refer to residential use, although the same MCL may be applied for non-residential use.
For example, the MCL for lead is 15 µg/L; MCLs are also set for other contaminants such as arsenic and radium.
According to the EPA, “the highest MCLG is the level of a contaminant in drinkable water that does not pose a substantial health risk.”
Therefore, the EPA sets an MCLG based on the lowest level at which no adverse health effects are observed in people who drink large amounts of contaminated water over a long period.
For example, if it is determined that one mg/L of lead causes no adverse health effects in people who drink large amounts over a long period, then the MCLG for lead is set at one mg/L.
How To Test for Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
The total dissolved solids (TDS) of water is the number of dissolved solids in a given volume of water. TDS is measured by weighing the water, heating it to a boil, and measuring the weight of water after it boils for one minute.
TDS can be used to calculate total hardness and pH. Hardness is an indicator of whether minerals are present in the water. If minerals are present in high quantities, hardness will increase, and pH will decrease.
If minerals are absent or present in low amounts, hardness will fall, and pH will increase.
How Is TDS Measured?
TDS, or total dissolved solids, measures the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances contained in a liquid.
In order to measure TDS, a sample of water is filtered to remove any suspended particles. Then the residue is weighed to determine the dissolved solid content.
The most common method for measuring TDS is with a conductivity meter, which uses an electrical current to measure the ability of the water to conduct electricity. The higher the concentration of dissolved solids, the greater the electrical conductivity.
You can also measure TDS with a refractometer, which uses the principles of refraction to determine the dissolved solid content. While both methods are accurate, conductivity meters are more commonly used due to their ease of use and lower cost.
Health Effects of Drinking High TDS Water
Drinking water is essential for good health, but not all water is created equal. For example, water with a high concentration of dissolved solids, or TDS, can have adverse health effects.
Ingesting high TDS water can lead to dehydration and gastrointestinal distress, as the body expends extra energy to process the solids.
In addition, high TDS water can damage tooth enamel and contribute to kidney stones. Furthermore, water with a high TDS level may contain harmful contaminants, including heavy metals and pesticides.
As a result, it is essential to be aware of the TDS level of your drinking water and take steps to filter out impurities, if necessary. By ensuring that you are drinking clean, safe water, you can help prevent health problems and save money.
Can You Drink Zero TDS?
Zero TDS water is simply water with all of its dissolved solids removed. You can do this through reverse osmosis, which uses a semi-permeable membrane to filter out impurities.
While zero TDS water is safe to drink, it can be less healthy than water with a moderate level of dissolved solids. Zero TDS water is unhealthy because many of the minerals and nutrients removed along with the dissolved solids are beneficial.
How Do I Lower the Total Dissolved Solids in My Tap Water?
If you have a kitchen faucet, you can try running the water for a few minutes. Running water will help remove some of the minerals from your tap water. If you cannot do this, you can try boiling your tap water for about five minutes.
Boiling water will also help remove some minerals and other substances from your water. However, you should not boil your drinking water for extended periods, as doing so can damage it over time.
Can I Filter My Water?
There are many different filters that you can use to reduce the TDS in your tap water. You can even go as far as installing one inside your home or business if needed. The most common types of filters include:
Inline filters:
These are installed in line with your faucet and use a filter cartridge that is replaced every month. These filter out many different contaminants, but they typically only filter out up to around 50-60 gallons of water.
Under-the-sink Filters:
These filters are installed under your sink and provide a large capacity. They filter out up to 300 gallons of water before needing to be replaced. These filters are usually more expensive than the inline type, but they can last for more extended periods.
Does Boiling Water Reduce TDS?
Boiling water does not remove all of the TDS from your water supply; however, it does remove some. This is why the EPA recommends that you boil tap water for at least one minute before drinking it.
Can a Sand Filter Reduce TDS?
Sand filters can reduce the TDS in your water supply by removing sediment, typically the most significant contributor to high levels of TDS in your water. However, sand filters can be difficult to clean and maintain.
Most commercially available models require you to change the sand every three months manually. If you have a large family or a lot of guests over for dinner, this may not be practical for you.
Can a UF Filter Remove TDS?
UF filter can remove most of the TDS from your water supply. UF filters effectively eliminate TDS, and they are widely used in homes today. However, UF filters do not remove all contaminants from your water supply that other types of filtration systems remove.
The most common pollutants UF filters cannot remove are pharmaceuticals and hormones, so bottled water is commonly used.
Does a Nano Filter Reduce TDS?
UF filters are the most common type of water filter that you will find in homes today. UF filters effectively remove TDS from your water supply, but they do not remove all contaminants from your water supply.
There are other types of filtration systems available today that can remove TDS, but they are more expensive than UF filters. The most common types of filtration systems that you will find in homes today include:
Water Softener:
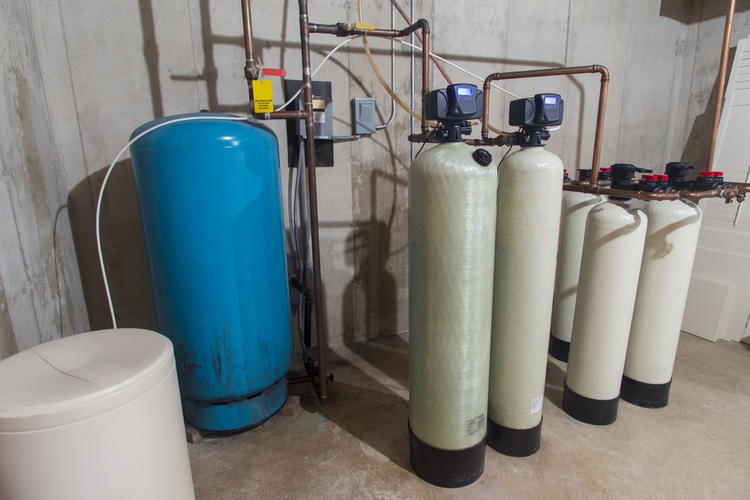

Softeners work by removing calcium and magnesium ions from your water supply; eliminating calcium and magnesium results in soft water with a lower TDS level than what is naturally occurring in groundwater.
Water softeners also reduce iron and manganese levels, found at high concentrations in well water. You can use a water softener to reduce TDS levels if you have a well as your source of drinking water or if you live near areas with high levels of naturally occurring minerals. Water softeners are relatively inexpensive and easy to install.
Softeners work by removing calcium and magnesium ions from your water supply. This results in soft water with a lower TDS level than what is naturally occurring in groundwater. Water softeners also reduce iron and manganese levels, found at high concentrations in well water.
You can use a water softener to reduce TDS levels if you have a well as your source of drinking water or if you live near areas with high levels of naturally occurring minerals.
Water softeners are relatively inexpensive and easy to install. Distillation – Distillation is the process of boiling water until it turns into steam, which then condenses back into liquid form under pressure, leaving the impurities behind.
Distillation
Distillation is an effective way to remove contaminants such as chlorine, but it does not remove all of the pollutants present in your drinking water supply. The UF filter removes most of these contaminants, while distillation removes some but not all of them.
Distillation is the process of boiling water until it turns into steam, which condenses back into liquid form under pressure, leaving the impurities behind. Distillation is an effective way to remove contaminants such as chlorine, but it does not remove all of the pollutants present in your drinking water supply.
The UF filter removes most of these contaminants, while distillation removes some but not all of them.
Reverse Osmosis
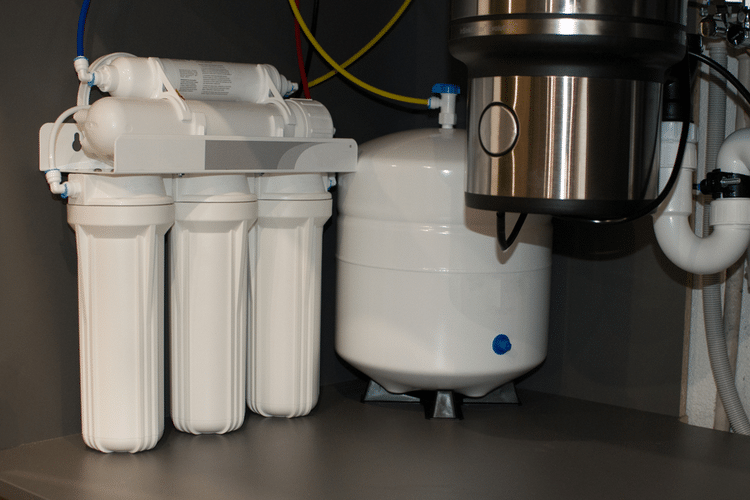

Reverse Osmosis (RO) uses a purer form of salt than distillation and extracts metals and other impurities from drinking water supplies.
RO is a good choice if you have many contaminants in your water supply or if you live near areas with high levels of naturally occurring minerals. However, RO systems are relatively expensive and require a lot of maintenance.
However, RO systems are relatively expensive and require a lot of maintenance. Spring Water – Spring water is water that has been purified and stored in a natural underground aquifer. It does not contain many impurities, but some residual minerals may cause mineral buildup over time.
Does Water Softener Reduce TDS?
Water softeners do not reduce TDS because TDS is not a measure of hardness. TDS measures the number of dissolved solids in water, and hardness is just one type of dissolved solids.
Water softeners increase the number of dissolved solids in your water by replacing calcium and magnesium with sodium.
What Is The Difference Between TDS and PH?
TDS is a measurement of the total dissolved solids (TDS) in water, while PH is a measurement of the acidity or alkalinity of the water. Therefore, the TDS level in your water supply will be higher than the PH level if it contains more TDS.
The PH level will be higher than the TDS level if it contains more alkalinity. Therefore, if your water supply is high in both TDS and PH, you may have many minerals in your water supply.
Great article. Thank you!