Nitrates, naturally occurring compounds that consist of nitrogen and oxygen atoms, have become a serious problem in America’s groundwater due to fertilizer runoff. The Environmental Work Group’s national nitrate analysis revealed that the municipal water in western states such as California and Arizona has an alarming nitrate presence.
The EPA’s (Environmental Protection Agency) public health goal and action limit for this compound is 10 parts per million (ppm) under its National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. If the nitrate presence in drinking water exceeds the set level, it could lead to blue baby syndrome in infants and carcinogenic effects in adults, which we’ll cover later.

So, for the wellbeing of you and your family, you should test your water for nitrates on a regular basis — especially if you depend on well water. If your water tests positive for nitrates, you can implement one of the methods we discuss below or opt for a state-of-the-art water filtration unit.
3 Effective Methods for Removing Nitrates From Water
Currently, there are three effective water treatment solutions for removing nitrates from water: distillation, reverse osmosis, and absorption.
Distillation
Distillation, also commonly referred to as vapor distillation, is one of the most conventional water treatment methods. Yet, its efficiency is still uncontested because distillation reduces water just to hydrogen and oxygen atoms, i.e., to its purest state, so it’s also an excellent method for nitrate removal.
In industrial-scale distillation, there are two tanks and transfer pipes. The process goes as follows:
- The water is heated in the first tank until it completely turns into vapor.
- The vapor is transferred to a second tank.
- There, the vapor is condensed and cooled down until it returns to a liquid state.
As the distance between atoms increases in the water’s gaseous state, the impurities, including nitrate molecules, have nothing left to hold onto. So, once the gas cools down and becomes liquid again, all that’s left is hydrogen and oxygen atoms or pure water.
This method is mostly used in water treatment plants and for producing safe bottled water. However, there are also countertop distillers that make the process doable at home.
The Waterwise 4000 Countertop Distiller is one of the best products in this category. It has a one-gallon capacity, distills 0.25 gallons per hour, is made of stainless steel, and features an ergonomic handle.
You can head to our list of the best countertop distillers to explore further options.
However, there’s a drawback to distillation. As it reduces water to just hydrogen and oxygen, it removes essential minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium. That’s why we don’t consider distilled water as a great option for drinking.
Reverse Osmosis
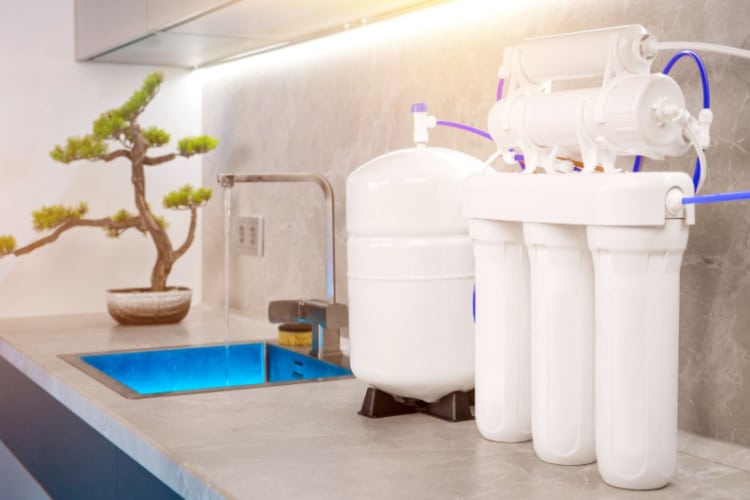

Reverse osmosis is one of the most popular and effective water treatment methods. It reduces the levels of many contaminants, including heavy metals, volatile organic compounds, and nitrates with remarkable success rates.
Reverse osmosis units feature a semipermeable membrane that has microscopic pores (usually 0.0001-micron). The devices use pressure to push the incoming water through this membrane. Thanks to the microscopic size of the pores, contaminants that have a molecular structure, like nitrates, are blocked entry.
AquaTru Countertop Reverse Osmosis System is the best reverse osmosis system. It’s certified by the National Sanitation Foundation, it’s compact, so you can easily move it, and it purifies a gallon of water in 12 to 15 minutes.
For other reverse osmosis options, check out our detailed guide.
We should warn you that reverse osmosis has the same disadvantage as distillation: it reduces the mineral levels in water. Additionally, it produces acidic water, and you might need to install a water alkalizer to reverse that.
Absorption

This technique uses an electrical charge that attracts contaminants with an ionic structure such as lead, arsenic, and nitrates. It then traps these contaminants’ molecules in long-lasting bonds.
Nitrates have a negative electrical charge, so the absorbent media that removes these compounds should have a positive charge.
Currently, only a handful of water treatment devices that feature gravity filtration (meaning water pitchers and some countertop filtration units) offer such absorbency in their proprietary technologies. However, the few that do tend to be the best on the market.
Case in point, theClearly Filtered Water Pitcher, the best water filter pitcher you can find, uses this absorption method in its Affinity Filtration technology. The results speak for themselves- the pitcher reduces nitrates with a staggering rate of 99.9%. If you want to have nitrate-free drinking water, this is one of your best bets.
How Nitrates Contaminate Water
Nitrogen is an extremely present element in nature. It makes up 78% of the air that we breathe. When this element reacts with water, it forms ammonium, and when it reacts with oxygen, it produces nitrates.
Nitrates are quite mobile in nature, so they don’t dissolve in water and aren’t absorbed by soil. However, there are plants and bacteria that absorb and recycle nitrates in different forms (sometimes as nitrates and sometimes as harmless nitrogen oxide gas).
However, the most likely cause of nitrate contamination, especially in US well water, is agricultural practices. Most fertilizers feature high amounts of nitrates that are pre-dissolved in water.
When the fields are fertilized at the right time, the plants are likely to absorb the nitrates to a higher extent. However, if the timing is wrong (as stated in the study conducted by the University of Arizona), the pre-dissolved nitrates will run off through the soil and find their way into the area’s water table.
This is why groundwater in agricultural areas is nitrate-rich. It also affects municipal water supplies that rely on groundwater like Arizona’s.
Additionally, human and animal waste have lots of nitrogen. The body of nitrogen in waste is likely to form nitrates in septic systems, and if there’s a septic tank close by your well or aquifer, it’s likely to contaminate your water supply with nitrates.
The Effects on Health from Nitrates in Drinking Water
The EPA regulates the nitrate presence in drinking water because if it’s higher than 10 ppm, it can cause death for infants and children below age six. Some symptoms of nitrate poisoning in babies are shortness of breath and blue baby syndrome, a condition in which a baby’s skin turns blue due to high nitrate intake and poorly oxygenated blood, also referred to as methemoglobinemia.
Besides its detrimental effects on infants, prolonged nitrate exposure can cause serious problems in adults. The Minnesota Department of Health lists depression, muscle weakness, nausea, increased heart rate, and abdominal cramps as symptoms of nitrate poisoning in adults.
According to public health authorities such as the EPA and the Minnesota Department of Health, research regarding the connection between nitrates in drinking water and risk of cancer isn’t conclusive yet. However, a 2018 study shows there’s at least a correlation between nitrate presence in water and elevated risk of colorectal cancer.
A 2020 study makes a connection between nitrates and other types of cancer, such as brain tumors and stomach cancer. The study concludes that there’s a link between nitrate dosage in water and stomach cancer, though it states that “there was an association only between the risk of brain cancer & glioma and colon cancer and nitrate consumption.”
Conclusion
Nitrates are naturally occurring compounds that don’t dissolve in water, but when pre-dissolved nitrates are utilized as fertilizers at the wrong time, they leak into local water tables. Septic tanks are another likely cause of nitrate contamination. That’s why nitrate contamination is a massive problem in areas where people and municipalities depend on groundwater.
While in controlled quantities, it’s not something to worry about, a nitrate presence higher than 10 ppm in drinking water poses a serious threat to the health and well-being of infants, children, and adults.
So, to keep yourself and your family safe, it’s imperative to remove this compound from drinking water. We recommend purchasing a water filtration unit that works on the principle of distillation, reverse osmosis, or absorption.